Current Affairs is an equally important section containing weightage of 20 questions in Railway Group-D Exam 2018 and has an even more abundant importance in some other exams conducted by SSC. Few of the questions were asked from Important chairpersons in different fields. For Railway Group-D Exam 2018, important awards, current affairs etc, so here we are with notes on Council of Ministers. So you should know persons who is who so that you can score well in the current affairs section.



COMPOSITION AND STRUCTURE OF ATMOSPHERE
The atmosphere is a thin envelop of gases surrounding the Earth thta forms a protective boundary between the outer space and the biosphere generally considered to be below 480km.
It is mixture of gases that is odorless, colourless,tasteless, and formless, blended so thoroughly that it behaves like a single gas.
The atmosphere is composed of:
- Nitrogen (78.09%),
- Oxygen (20.95%),
- Argon(0.93%),
- Other gases(0.03%)
- Air pressure
As regards the character of the tempeature changes with height and other factors the atmosphere is divided into several spheres as follows-
- -TROPOSPHERE
- -STRATOSPHERE
- -MESOSPHERE
- -THERMOSPHERE OR IONOSPHERE
- -EXOSPHERE
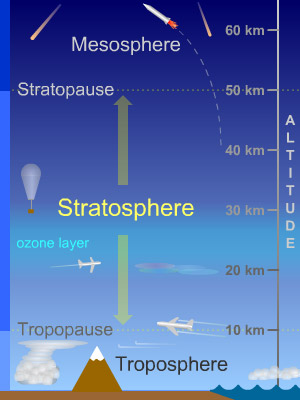
TROPOSPHERE:
- This layer is the most important layer of the atmosphere.
- Its average height is 13 km.
- The air we breathe exists here.
- Almost all the weather phenomena like rainfall, fog and hailstorm occur in this layer.
- Tropopause - it is the layer that separates the troposphere from the stratosphere.In the troposphere, the temperature generally decreases with height, whereas above the tropopause, the temperature no longer decreases.
STRATOSPHERE:

- Above the troposphere lies the stratosphere.
- It extends up to a height of 50 km.
- This layer is almost free from clouds and associated weather phenomenon, making conditions most ideal for flying aeroplanes.
- One important feature of the stratosphere is that it contains a layer of ozone gas, which protects us from the harmful effect of the sun rays.
MESOSPHERE:
- This is the third layer of the atmosphere and lies above the stratosphere.
- It extends up to the height of 80 km.Meteorites burn up in this layer on entering from the space.
- It is the coldest layer of the atmosphere.
THERMOSPHERE:
- In thermosphere temperature rises very rapidly with increasing height.
- The ionosphere is a part of this layer. This layer helps in radio transmission.
IONOSPHERE:
- It lies immediately above the mesosphere and extends from 80 to 400 km above the Earth's surface.
- The ionosphere is the part of the Earth's upper atmosphere, where ions and electrons are present to affect the propagation of radio waves.In fact, radio waves transmitted from the earth are reflected back to the earth by this layer.
- This layer contains electrically charged air that protects the Earth from falling meteorites as most of them burn out in this region.
EXOSPHERE:
- The uppermost layer of the atmosphere is known as Exosphere. This layer has very thin air.
- Light gases like helium and hydrogen float into space from here.
- It extends from the top of the thermosphere up to 10,000 km (6,200 mi).



No comments:
Post a Comment