Dear Students, As SSC CGL Tier-I 2017 is going to be conducted in the month of August 2017. For GA Part we are providing all types of topics and notes. Today, in this post we are providing to you study Notes on Biology notes for SSC CGL and MTS Exam. Sometimes questions are asked from this topic as well, So memorize all these articles and score better in the exam. You can also study Quizzes on all GA subjects.
Blood
The main functions of blood are to transport oxygen, carbon dioxide, water, nutrients, hormones and waste around the body. Blood also fights infection and regulates temperature.
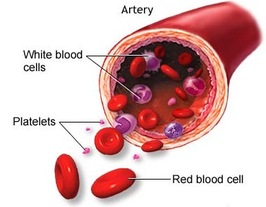
Composition of blood:
1. Plasma constitutes for about 54% of our blood. 92% of it is water.
2. White blood cells and platelets constitute for about 1% of our blood.
3. Red blood cells constitute for about 45% of our blood.
Circulatory System
Circulation of Blood through the heart:
Systemic Vein ⇨ Sinus Venosus ⇨ Right Auricle ⇨ Right Ventricle ⇨ Pulmonary Artery ⇨ Lungs ⇨ Pulmonary Vein ⇨ Left Auricle ⇨ Left Ventricle ⇨ Trunchus Arteriosus ⇨ Systemic Circulation
Open circulatory systems allow the blood flow out of the vessels before returning to the heart via ostia. (no veins involved)E.g. insects
Systemic Vein ⇨ Sinus Venosus ⇨ Right Auricle ⇨ Right Ventricle ⇨ Pulmonary Artery ⇨ Lungs ⇨ Pulmonary Vein ⇨ Left Auricle ⇨ Left Ventricle ⇨ Trunchus Arteriosus ⇨ Systemic Circulation
Open circulatory systems allow the blood flow out of the vessels before returning to the heart via ostia. (no veins involved)E.g. insects

• Closed circulatory systems don’t allow the blood to leave the blood vessels E.g. humans advantages include faster and controlled delivery of oxygen and nutrients which allow for longer periods of activity.
Important Points:
➧Aorta
The largest artery in the body. It carries oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to vessels that reach the rest of the body.
➧Atria
The chambers of the heart, to which the blood returns from the circulation.
➧Capillaries
The smallest of the body's blood vessels. Oxygen and glucose pass through capillary walls and enter the cells. Waste products such as carbon dioxide pass back from the cells into the blood through capillaries.
➧Cardiac Valves (Heart Valves)
Any of the four heart valves that regulate the flow of blood through the chambers of the heart.
➧Deoxygenated Blood -> Oxygen-poor blood.
➧Heart Ventricles
The lower right and left chambers of the heart.
➧Interventricular Septum
Interventricular septum is the stout wall separating the lower chambers (the ventricles) of the heart from one another.
➧Lungs
One of a pair of organs in the chest that supplies the body with oxygen, and removes carbon dioxide from the body.
➧Myocardium
The muscular substance of the heart; the middle of the three layers forming the outer wall of the human heart.
➧Oxygenated Blood -> Oxygen-rich blood.
➧Pulmonary Artery
The pulmonary artery and its branches deliver blood rich in carbon dioxide (and lacking in oxygen) to the capillaries that surround the air sacs.
➧Pulmonary Circulation
The circulation of the blood through the lungs.
➧Pulmonary Veins
The veins that return the oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
➧Superior Vena Cava
The large vein that carries blood from the head, neck, arms, and chest to the heart.
➧Vena Cava
A large vein which returns blood from the head, neck and extremities to the heart.
➧Endothelium is the innermost layer of blood vessels that consists of just a single layer of cells.
Important Points:
➧Aorta
The largest artery in the body. It carries oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to vessels that reach the rest of the body.
➧Atria
The chambers of the heart, to which the blood returns from the circulation.
➧Capillaries
The smallest of the body's blood vessels. Oxygen and glucose pass through capillary walls and enter the cells. Waste products such as carbon dioxide pass back from the cells into the blood through capillaries.
➧Cardiac Valves (Heart Valves)
Any of the four heart valves that regulate the flow of blood through the chambers of the heart.
➧Deoxygenated Blood -> Oxygen-poor blood.
➧Heart Ventricles
The lower right and left chambers of the heart.
➧Interventricular Septum
Interventricular septum is the stout wall separating the lower chambers (the ventricles) of the heart from one another.
➧Lungs
One of a pair of organs in the chest that supplies the body with oxygen, and removes carbon dioxide from the body.
➧Myocardium
The muscular substance of the heart; the middle of the three layers forming the outer wall of the human heart.
➧Oxygenated Blood -> Oxygen-rich blood.
➧Pulmonary Artery
The pulmonary artery and its branches deliver blood rich in carbon dioxide (and lacking in oxygen) to the capillaries that surround the air sacs.
➧Pulmonary Circulation
The circulation of the blood through the lungs.
➧Pulmonary Veins
The veins that return the oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
➧Superior Vena Cava
The large vein that carries blood from the head, neck, arms, and chest to the heart.
➧Vena Cava
A large vein which returns blood from the head, neck and extremities to the heart.
➧Endothelium is the innermost layer of blood vessels that consists of just a single layer of cells.
➧Veins are blood vessels that carry blood to the heart in an even flow. They have thin walls large lumens and valves.

• The human circulatory system consists of two circuits systemic and pulmonary.
• The coronary artery carries blood to the heart muscle from the aorta. (coronary vein)
• The hepatic artery carries blood to the liver. (hepatic vein)
• The renal arteries carry blood to the kidneys. (renal veins)
• The mesenteric arteries carry blood to the small and large intestines.

• The carotid arteries supply blood to the head. (jugular veins)
• The subclavian arteries supply blood to the arms. (subclavian veins)
• The iliac arteries carry blood to the legs. (iliac veins)
• A portal system is a network of capillaries in one organ or tissue joined to another network of capillaries in another organ or tissue via a vein or veins.
• A pulse is the alternate contraction and relaxation of an artery as blood passes through it.
• Blood pressure is the force blood exerts on the walls of blood vessels.
• A sphygmomanometer is used for measuring blood pressure(normally 120/80 mmHg)
• Atherosclerosis is the hardening of artery walls due to a build-up of fatty deposits.
• Smoking causes heart rate and blood pressure to increase. Diet high in saturated fats increase blood pressure and atherosclerosis. Exercise helps lower blood pressure.

To be continued..



No comments:
Post a Comment